Treating diarrhea naturally with the Indian madder
07/23/2018 / By RJ Jhonson
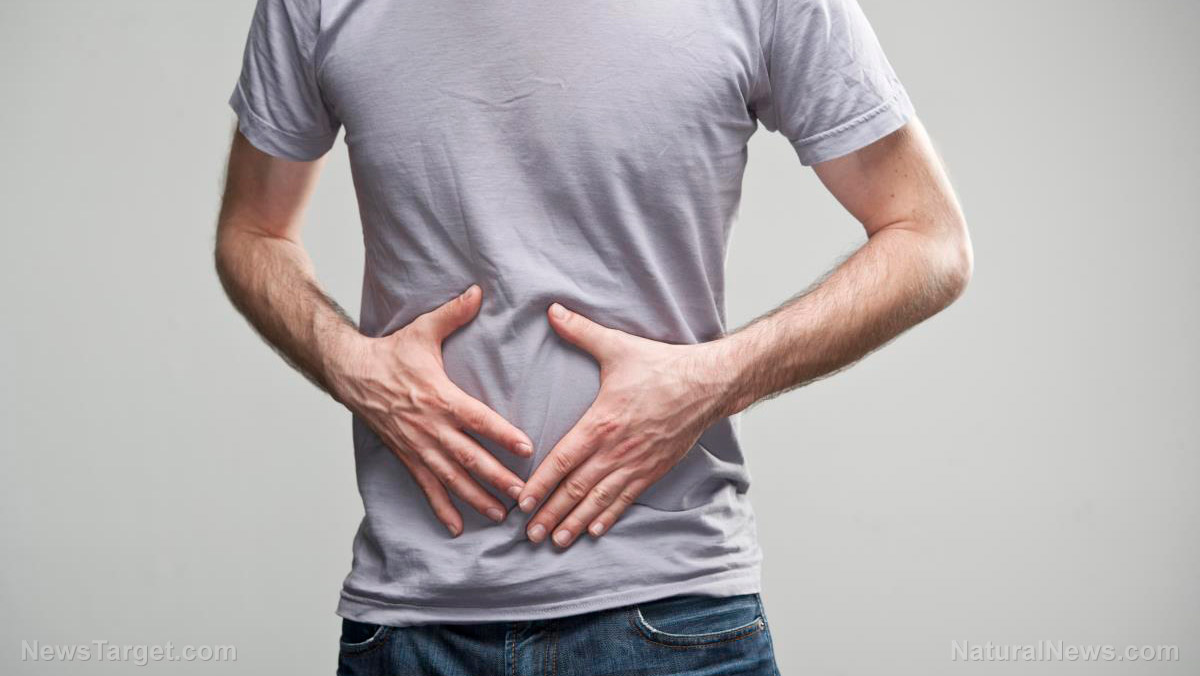

A study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine confirmed the anti-diarrheal and anti-inflammatory effects of Rubia cordifolia, also known as the Indian madder.
The study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei province, China.
- R. cordifolia has long been used in traditional Chinese medicine as a treatment for diarrhea, however, no research has been conducted to prove its medicinal benefits.
- The researchers created several rat models to determine the effects of aqueous extract of R. cordifolia’s aerial parts (AERCAP) on senna leaf- and castor oil-induced diarrhea. Rat models were also used to determine intestinal transit, acute toxicity, and AERCAP’s effects on colonic inflammation induced by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS).
- In both senna leaf- and castor oil-induced diarrhea tests, the scientists administered an initial dosage (0.4 mL/kg senna leaf decoction or 0.2 mL/kg castor oil). They took 50 of those that developed diarrhea and divided them into five groups: one control treated with distilled water, one treated with loperamide, and three treated with AERCAP in varying doses (500 mL, 1,000 mL, and 2,000 mL). The rats were treated with another dose of senna leaf decoction after 30 minutes and had their feces examined to determine the severity of their diarrhea. The procedure was repeated for the castor oil test.
- To determine AERCAP’s anti-inflammatory effects, rats were divided into six groups: one healthy group, one TNBS group, one dexamethasone group, and three AERCAP group in varying doses (500 mL, 1,000 mL, and 2,000 mL). After five days, TNBS dissolved in ethanol was administered through the animals’ anus. The rats were sacrificed after 72 hours and their colon examined for inflammation.
- The scientists discovered that AERCAP delayed the onset of semi-solid feces in senna leaf-induced diarrhea and inhibited the propulsive movement in castor oil-induced diarrhea.
- Examination of the animals’ colon revealed that those treated with AERCAP showed decreased damage caused by TNBS.
- All doses tested showed no signs or mortality or toxicity, indicating that AERCAP is non-toxic.
The scientists concluded that AERCAP has anti-diarrheal and anti-inflammatory effects, which confirm its role and usage in traditional Chinese medicine.
Read the full text of this study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Gong XP, Sun YY, Chen W, Guo X, Guan JK, Li DY, Du G. ANTI-DIARRHEAL AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITIES OF AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF THE AERIAL PART OF RUBIA CORDIFOLIA. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2017;17(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1527-9
Tagged Under: anti-diarrheal, anti-inflammatory, diarrhea, good herb, herbal remedies, Indian madder, natural medicine, natural treatment, Rubia cordifolia